Interest Rate Sensitive Stocks

Interest rates are a fundamental driver of economic activity, influencing everything from consumer spending to corporate investment. In the stock market, changes in interest rates can ripple through various sectors, altering profit margins, affecting debt costs, and shaping investor sentiment. While the effects of these changes are not always immediate or uniform across industries, some sectors—particularly those that are capital-intensive—are especially sensitive to interest rate shifts.
Known as “interest rate-sensitive stocks,” these companies typically face higher debt-servicing costs and potential earnings pressures when interest rates rise. Such stocks are generally characterized by a high cost of debt servicing and relatively high dividend yields. This article aims to explore the impact of lower interest rates on interest rate-sensitive stocks, with a focus on the U.S. telecommunications industry.
Executive Summary
The analysis reveals that telecommunications stocks, particularly those with high dividend yields, tend to benefit in a lower interest rate environment, as reduced borrowing costs ease the burden on debt servicing. AT&T Inc., Cogent Communications Holdings, Inc., and Verizon Communications Inc. are identified as key interest rate-sensitive stocks within this industry and are expected to see positive market performance if interest rates continue to fall in the coming months. This analysis underscores the importance of both macroeconomic factors and company-specific details in assessing investment opportunities in the telecommunications sector.
Causal Links
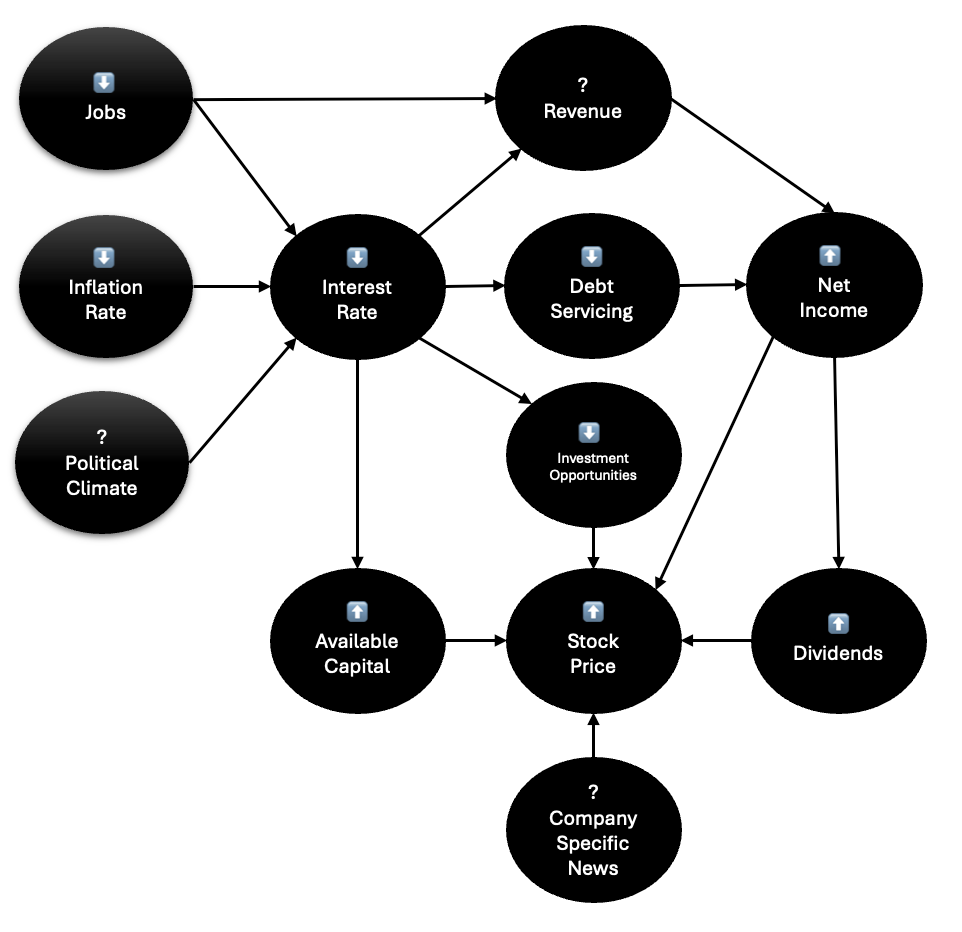
The proposed causal link for this analysis is illustrated in the figure above, demonstrating how inflation and employment data ultimately impact the stock prices of companies. Typically, a decrease in job numbers coupled with subdued inflation would prompt the Federal Reserve to lower interest rates to avert a recession. The Fed's mandate is to maintain inflation within a narrow range and ensure full employment, establishing a clear relationship between these economic indicators. Generally, lower employment figures translate to reduced revenue for companies, as fewer people have stable jobs to purchase goods and services. However, this impact can vary significantly depending on the price elasticity of those products and services.
Lower interest rates have two primary effects: company-specific impacts and broader implications for the investment landscape. There are two main impact on the company of lower interest rates. First, reduced rates usually lead to higher revenues, as consumers have easier access to credit to spend on goods and services. Nevertheless, this revenue boost may be counterbalanced by weak job data, as there is often a lag before employment figures improve following a rate cut. The second company-specific effect is lower debt servicing costs. If a company can maintain or stimulate revenue through lower interest rates, its net income typically increases, resulting in greater free cash flow for dividends. Higher dividends and improved earnings prospects generally contribute to rising stock prices.
On the other hand, in the investment world, lowering interest rates has two significant effects. Firstly, it expands the pool of available capital, as lower rates make it easier to service debt with income generated from investments. Secondly, low interest rates reduce the number of attractive investment opportunities. In this environment, the bond market often yields only marginal returns, which can be inadequate when considering inflation. As a result, both factors can drive up stock prices, as more capital becomes available for investment and the stock market emerges as the most viable option for achieving respectable real returns.
How are interest rate-sensitive stocks special?
Interest rate-sensitive stocks are distinctive in that they are often highly capital-intensive, and the products and services they provide tend to be relatively inelastic. For instance, AT&T must finance its substantial capital expenditure for its 5G network. However, regardless of the interest rate environment, consumers typically continue to maintain their subscriptions. For example, lowering interest rates does not directly translate to consumers upgrading their network plans. As a result, these companies are more vulnerable to fluctuations in interest rates, as a significant portion of their operational costs stems from servicing the debt incurred for their capital investments. Therefore, all else being equal, one would expect net income to increase, leading to higher stock prices.
Another key differentiating factor is that these interest rate-sensitive stocks often offer higher dividend yields. When investment opportunities in bonds are limited, and cash flow becomes a necessity for investment firms, these stocks present a compelling alternative. This increased demand for high-yield dividend stocks can further drive up their prices, all else being equal.
Methodology in Proving Causal Link
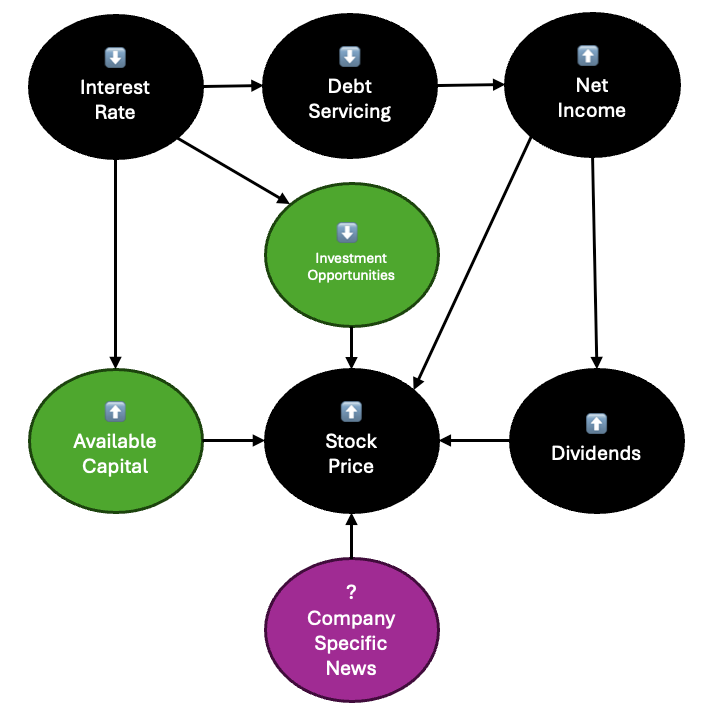
To establish a causal link between interest rates and the stock prices of interest rate-sensitive stocks, it is essential to consider other influencing factors. Specifically, the effects of interest rates on the broader investment landscape, illustrated by the green colored nodes, and company-specific news, represented by the plum colored node, must be accounted for.
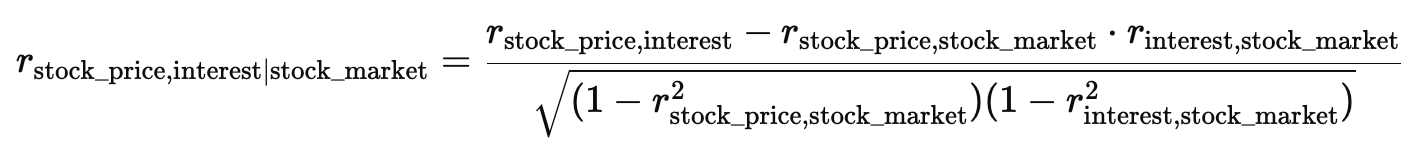
The general impact of interest rates can be estimated by the general movement of the stock market. High availability of capital with a smaller pool of investments would typically results in good performance by the stock market. The partial correlation between stock prices and interest rates, while controlling for the stock market, can be computed to isolate the impact of the changes in interest rates from the impact of the general market to the stock. The S&P 500 will serve as the proxy of the stock market to gauge the impact on the investment landscape. Rank-sum correlation will be employed, ensuring that the analysis focuses on relative rankings rather than absolute values.
To account for the impact of company-specific news, the analysis will be conducted over multiple years, from 2008 to 2023. Additionally, it will be analyzed using the following stocks to further mitigate the influence of company-specific events:
- AT&T Inc (T)
- Cogent Communications Holdings, Inc. (CCOI)
- Frontier Communications Parent, Inc. (FYBR)
- Lumen Technologies, Inc. (LUMN)
- T-Mobile US Inc (TMUS)
- Verizon Communications Inc. (VZ)
Data for the adjusted stock prices and the S&P500 index were obtained from Yahoo Finance using a community-built scraper YFinance. 10 year treasury yields published by the Federal Reserve is used as a proxy for interest rates. A 20-year period is chosen, as it is typically sufficient for financing long-term projects within the telecom industry. For example, in the 2024 2nd Quarter Earnings of AT&T Inc , the weighted average maturity of its long term debt is 16 years (Q2 Investors Report)
Causal Link Results
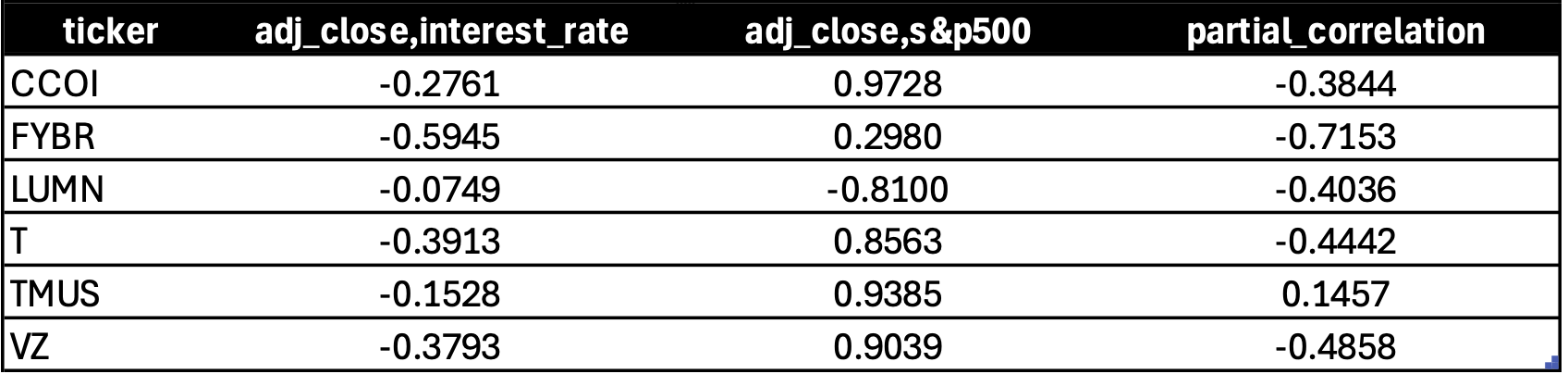
The rank correlation analysis between the adjusted closing prices, interest rates, and the S&P 500 index is presented above. Generally, even prior to adjusting for the impact of the market, all stocks exhibited a negative correlation between stock prices and the interest rates. With the exception of Lumen Technologies and Frontier Communications, all stocks show a strong positive correlation with the S&P 500 index, indicating they are significantly influenced by market returns.
After controlling for the impact of the S&P 500 index using partial correlation, the analysis find that, except for T-Mobile US Inc., all other stocks exhibit a strong negative correlation between interest rates and their adjusted closing prices. This reinforces the thesis that these stocks are indeed significantly affected by changes in interest rates.
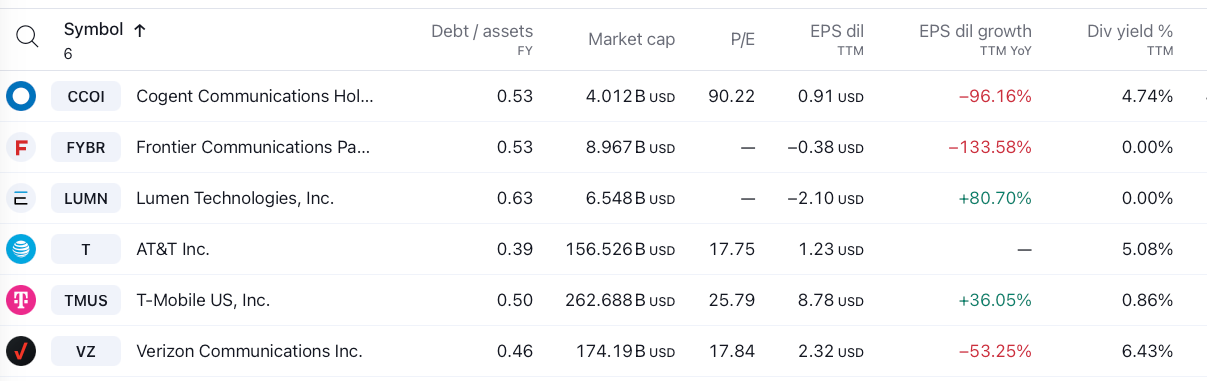
Upon examining company-specific data, it becomes clear that Lumen Technologies, Inc., Frontier Communications Parent, Inc., and T-Mobile US Inc. do not share the same dividend yield levels as other players in the telecommunications industry. Due to their very low to non-existent dividend yields, they are unlikely to be classified as interest rate-sensitive stocks. The strong negative correlations observed for Lumen Technologies, Inc. and Frontier Communications Parent, Inc. are therefore likely spurious, as they do not align with the causal link established earlier.
Recent Development
The graph above shows the cumulative gains over 1 year running when invested in S&P500 compared to the 3 interest sensitive stocks identified in the analysis. The graph is updated every day with the recent prices pulled from Yahoo Finance. This section aims to evaluate the analysis above over time.
November 3, 2024: For the most part, the S&P500 has outperformed these interest sensitive stocks during rising treasury rates environment. However, we can see that A&T recently started to outperformed the S&P500. This coincides with the recent decrease in treasury rates.
Conclusions
The use of partial correlation over an extended period—including phases of rising and falling interest rates across multiple companies—provides compelling evidence of a causal relationship between interest rates and the stock prices of interest rate-sensitive companies. Importantly, the analysis reveals that not all stocks that are classified under the Telecommunications industry are truly sensitive to interest rate changes; those lacking relatively high dividend yields do not meet this criterion. AT&T Inc., Cogent Communications Holdings, Inc., and Verizon Communications Inc. do meet this threshold and are projected to benefit from anticipated rate declines, suggesting an increase in their market value in the months ahead.
